What Is Dravidian Style Of Architecture?
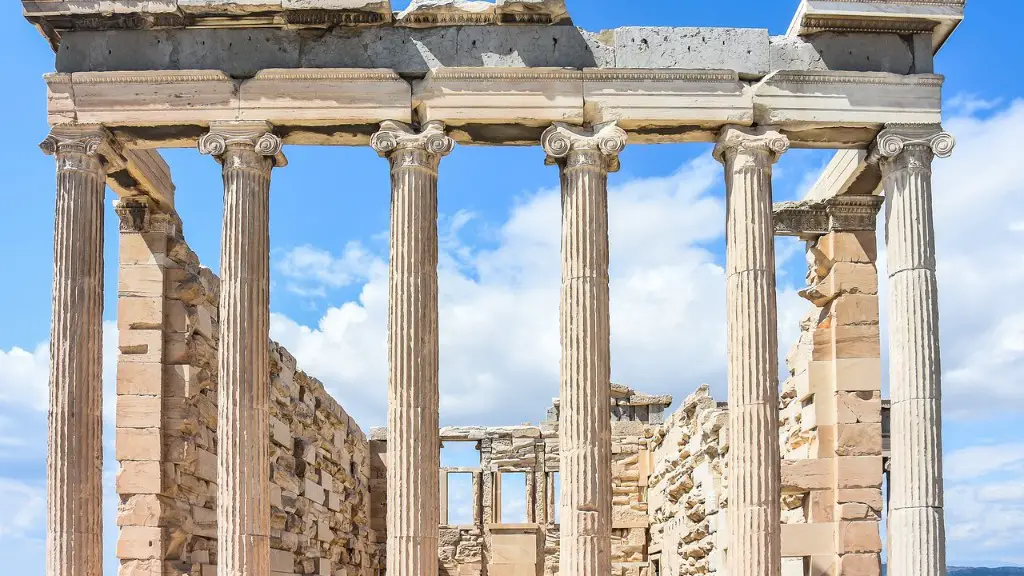
The Dravidian style of architecture is an ancient form of architecture and art form that originated in southern India around 1500 BC. This architectural style has been used throughout India and Sri Lanka for centuries and is still popular today. It is characterized by its distinctive iconography, deep verticals, and horizontals, large open courtyards with colonnaded verandas, ornate pillars and arches, and high towers, often topped with a dome.
Dravidian style of architecture is also known for its heavy and often intricate decoration, which may include intricate stone carvings and sculptures. The most characteristic features of Dravidian architecture are the gopuram, the meenakshi temple and the chariot temples, which are the most famous examples of Dravidian architecture. The gopuram is a tall, intricately carved tower that may have several stories and is often multi-tiered and decorated with a variety of symbols related to Hindu mythology.
The meenakshi temple is a large architectural complex that includes several shrines and buildings in the style of Dravidian architecture. It is located in the city of Madurai in Tamil Nadu and is believed to be one of the oldest temples in India. The chariot temples are temple complexes dedicated to Hindu deities and known for their grandiose scale. These buildings are usually surrounded by a large number of sculptural figures that are considered to be some of the most impressive examples of Dravidian art.
Dravidian style of architecture is believed to have had a strong influence on the buildings of other regions in India as well. Examples of such buildings include the Meenakshi temple in Bangalore and the Brihadeeswarar Temple in Thanjavur. This style of architecture has also had an influence on European and North American building styles, particularly in the United States. Some examples of buildings that have been influenced by Dravidian architecture are the White House in Washington, D.C. and the Taj Mahal in Agra.
One of the key elements that makes Dravidian architecture unique is the use of symmetry and balance. This style is often seen in the placement of structural elements and in the use of geometric shapes to create a visually balanced composition. These details help to create a sense of harmony and balance in the architecture, which is what makes it so appealing.
The materials used for Dravidian architecture also had to be of good quality and durable. Materials such as stone, bricks, and timber were commonly used. The ornamentation of the buildings was also extremely important and intricate carving, sculpture, and iconography were used to bring out the beauty of the architecture.
Influence Of This Style
The influence of the Dravidian style of architecture can still be seen in contemporary Indian architectural designs. Some modern patterns that are used, such as the gopurams, meenakshi temples and chariots, are drawn from this style and are still used extensively. The application of Dravidian iconography, however, has become much more subtle and is used to evoke a particular mood or atmosphere.
Modern architects have also been inspired by Dravidian architecture and have taken its characteristic styles and integrated them into their designs. This can be seen in the use of columns, arches and balconies in many modern buildings. These elements help add a sense of grandeur to a building and provide it with an elegant and timeless appeal.
The influence of Dravidian architecture is also being felt in the modern world. Many modern buildings around the world take cues from this timeless style, such as the Taj Mahal in Agra, India, the Pantheon in Rome, the Parthenon in Athens, and the US Capitol Building in Washington, D.C..
Preserving History
The preservation of Dravidian architecture is an important aspect of India’s cultural heritage. The government has taken steps to protect and maintain important historical buildings, including the Meenakshi temple in Madurai and the Brihadeeswarar Temple in Thanjavur. In addition, the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) is responsible for the ongoing protection and preservation of this important architectural heritage.
India is also home to a number of Dravidian-style buildings that have been inscribed as UNESCO World Heritage Sites. These include the Great Living Chola Temples, The Rock Shelters of Bhimbetka, and The Ellora Caves. These sites are testimony to the architectural achievements of the Dravidian people and the importance they placed on their art, architecture and culture.
In addition to the protection of important sites, the Indian government also provides grants to conserve and preserve Dravidian buildings. There are also various organizations that provide training and education in this style of architecture, as well as programs that promote its appreciation and understanding.
Education On The Dravidian Style
Education about Dravidian architecture is important for people to be able to appreciate its beauty and understand the significance of this cultural heritage. The Indian government has recognized the importance of education about Dravidian architecture and has included it in their school curriculums. There are also a number of courses and workshops available for people who are interested in exploring this style of architecture.
In addition, there are a number of books and websites devoted to the study of this style of architecture. These books and websites provide detailed information about the styles, features, and symbolism of Dravidian architecture. They also offer images and photographs of buildings constructed in this style.
The study of Dravidian architecture is an important part of understanding the culture and history of India. It is a reminder of the sophistication and sophistication of the people who once lived in the region. By understanding this style of architecture, we can appreciate the beauty of its forms and gain an insight into the history and culture of the Dravidians.
Current Popularity Of Dravidian Architecture
Today, Dravidian architecture is still popular in many parts of India, Sri Lanka and South East Asia. This style is often used in religious and private buildings, as it is believed to be spiritually important and auspicious. Many modern buildings have been built in the Dravidian style, including the Lotus Temple in Delhi and the Prime Minister’s Residence in New Delhi. This style of architecture is also increasingly being used for commercial buildings, as its elegant and timeless appeal continues to inspire and attract people.
In addition to being popular in India, the style of Dravidian architecture has also begun to gain popularity in the West. This style gives a sense of tranquility and peace and has been used in hospitals, universities, and other public buildings. In addition, it has become a popular choice of design for modern homes, as it can provide a sense of grandeur and sophistication.
Although the use of Dravidian architecture has declined in modern times, its appeal remains strong. This style of architecture is a reminder of the sophistication and elegance of India’s ancient culture, and its influence can still be seen today in many modern buildings.
Disadvantages And Limitations
Despite its popularity, Dravidian architecture does have some disadvantages. This style of architecture is often time-consuming and costly to construct, as it is based on intricate planning and skill. In addition, many of the traditional building materials used for Dravidian architecture are no longer available. As a result, many of the traditional methods for constructing and maintaining the buildings have been lost.
Another disadvantage of Dravidian architecture is that it is often difficult to modernize. For example, the use of modern materials, such as steel, concrete and glass, is often not compatible with the architecture and can look too modern or out of place.
Despite its limitations, Dravidian architecture remains an important and vibrant part of the Indian cultural heritage. It is a reminder of the sophistication and elegance of this ancient style, and its influence can still be seen in many modern buildings around the world.